What’s Inside?
Inside U-Nique Accounting’s Ultimate Guide to Inflation for Businesses, you’ll learn about the fundamentals of inflation, what potential concerns you should be aware of, and our recommended solutions to help prepare your business for an extended inflationary period.
What is Inflation?
The technical definition of inflation is the rate at which the value of a currency is falling and, consequently, the prices for goods and services are rising.
While we can’t see the value of our currency falling, what we can see – and definitely feel – are price increases. The most notable inflation pressure can be seen in energy and food. The costs to heat or cool our homes, fill up our vehicles, and feed our families.
Our needs as humans are not limited to just energy and food, we rely on healthcare, entertainment, transportation, and more for a comfortable life. Therefore, “inflation aims to measure the overall impact of price changes for a diversified set of products and services, and allows for a single value representation of the increase in the price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time,” according to Investopedia.
Currently that single value rate of inflation is surpassing most economists’ predictions. Also surpassing their predictions is the length of time we will experience inflation. What was once thought to only last through 2021 is now predicted to last far longer.
According to The Associated Press, “Higher prices will likely last well into next year, if not beyond.”
What Causes Inflation?
Inflation is usually caused when too much money is put into circulation by a central bank. However, the cause of our current inflation crisis is different in that a variety of economic disruptions, including a global pandemic-induced global lockdown, led to rising prices.
Similar to inflation during wartime, the abrupt demand for goods & services coupled with backed-up production & shipping has led to the highest price increase the United States has seen in forty years.
What Problems Will Inflation Cause for Businesses?
As a business owner, you may be bracing for impact as discussion of inflation swirls. Over the next few pages, we’ll detail out a few potential concerns to be aware of.
Inflation’s Impact On The Supply Chain
The booming economy of 2019 was a well-oiled machine. Manufacturers, retailers, and restaurants relied on what they needed to be delivered “just in time,” meaning they got just what they needed, when they needed it.
Just-in-Time (JIT) is a supply chain model that helps keep inventory costs low and the economy churning.
However, everything began to change in March 2020 with the start of a global lockdown economy.
From panic-buying consumer behavior, to a lack of shipping and production labor, onto various impactful natural disasters – the well-oiled machine began to tilt off course.
Fast forward to the end of 2021, and the supply chain chaos is only worsening. In fact, experts agree that supply chain issues will continue well into 2022.
Increasing demand (thanks to post-COVID spending, increasing wages, and the holiday season) coupled with a back-up in supply is only perpetuating the inflationary prices we see today.
It will become more and more difficult to discern the difference between opportunistic pricing, and genuine supply-demand increases.
Bottom Line: Businesses can continue to expect exaggerated delays in shipping times, a shortage of raw materials, an increase in raw material pricing, and a pile up of aging inventory in many cases. |
Inflation’s Impact on Purchasing Power
Unfortunately, a decline in purchasing power goes hand-in-hand with an increase in prices.
Inflation and purchasing power are two sides of the same coin.
Increase in Inflation = Decline in Purchasing Power
This means that the amount of money you have in your bank account today, will not purchase as many goods & services in the future.
As you can imagine, a decline in purchasing power can have tremendous short-term effects on both consumers and businesses.
As the value of the dollar decreases, so does the ability for everyday Americans to buy goods and services.
For many businesses, this can mean fewer products sold, and in turn, lower profitability over the next few years.
Bottom Line: Inflation will naturally decrease the value of the dollar, and your wallet will not stretch as far. Some businesses will opt to purchase large expenditures now. |

Inflation’s Impact on The Labor Market
It’s easy to think of salaries as independent of inflation, especially when you see that the minimum wage holds relatively steady year-to-year.
But the truth is inflation influences what a company pays its employees.
As your employee’s cost of living goes up, so does their restlessness regarding their current salary. They increasingly wonder if they are worth more and if they can make more by moving on.
At the same time, no business would be wise to pay too much. You’d lose profits that way, too, and eventually need to cut employees.
It’s important to realize that inflation hits businesses from many angles. Not only are raw materials on the rise, you’ll need to deal with high unemployment, so it’s hard to fill positions.
You may also have high employee turnover as remaining employees either burn out because you’re understaffed or find your competitors pay better.
Bottom Line: Inflation will increase minimum wage. Coupled with high unemployment rates and increasing restlessness post COVID-19, companies should expect to pay more to attract and retain top talent. |
Inflation’s Impact on Budgeting
Typically during this time of year, business owners across the United States sit down to evaluate the year in review, and plan a new budget for the year ahead.
During an inflationary period, especially one as abrupt as this, the moving pieces of the budget can feel impossible to nail down.
It’s hard to know at this point in time how the federal government will react, and in turn, slow the growing prices.
With the increase in cost of goods, along with the volatility of the current labor market, maintaining the same levels of profitability next year may not appear feasible.
Businesses will struggle to identify how much cash they’ll need to get through various scenarios, and the ability for customers to pay is yet to play out.
Check out our free How-to Keep More Cash In The Bank Guide to help stay on top of your cash flow management this year.
Bottom Line: Inflation impacts every aspect of the budget. We can assume sales levels will decrease, loan payments and cost of goods will rise, and labor wages will increase. However, the scenarios may change. |
Inflation’s Impact on Business Cash Flow and Profits
Speaking of cash flow, there is a chance that businesses will see a dramatic shift with their Cash Flow Conversion Cycle (CCC), which can spell havoc for working capital budgets and general cash flow in the business.
- What is Cash Flow Conversion Cycle (CCC)? Your Cash Conversion Cycle (CCC) is a leading indicator of how you are managing your cash flow. It will tell you how long it takes to realize positive cash flow from a sale. The lower your CCC, the better your cash management is.
During inflationary periods, companies tend to stock up on products in order to maximize the value of the dollar. At the same time, consumers buy less due to the fact that their dollars aren’t stretching as far.
The combination of these simultaneous events can lead to slower inventory turnover, and slower customer payments, which can increase the weeks – and even months – that businesses are left with a negative cash flow.
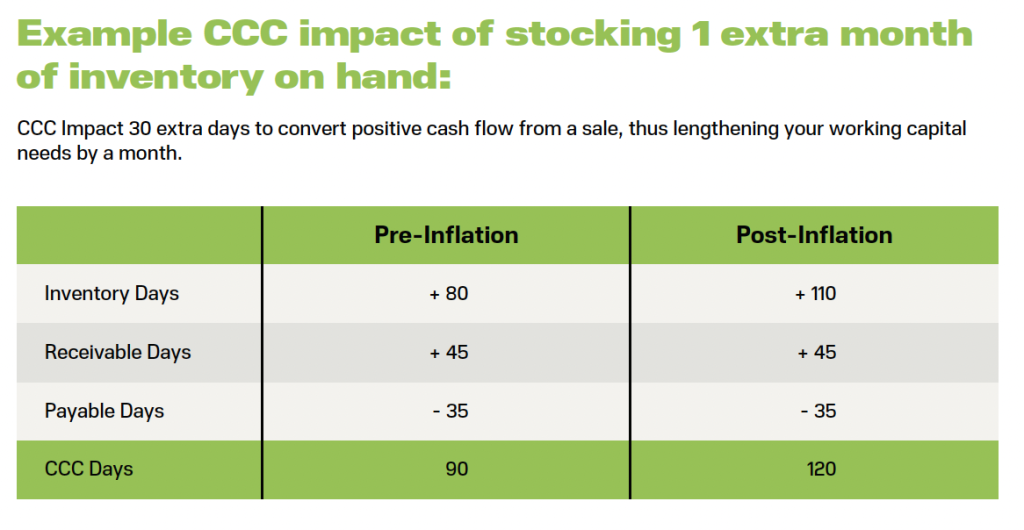
Bottom Line: Inflation is likely to impact the time in which you’re paid by customers. Businesses who haven’t planned for various scenarios, and those who aren’t monitoring cash flow in real-time can end up with months-on-end without cash in the bank. |
Inflation’s Impact on Interest Rates
In order to control the overwhelming increase in prices, the Federal Reserve will need to raise the fed funds rate.
As defined by The Balance, “The fed funds rate is the interest rate banks charge each other to lend Federal Reserve funds overnight. The nation’s central bank uses it in addition to other tools to promote economic stability by raising or lowering the cost of borrowing.”
Since late 2019, this rate has been on a decline. On March 15, 2020, the Fed lowered the rate to almost 0% on March 15, 2020 in an effort to boost the economy amidst the impending threat of the coronavirus pandemic.
Today, the rate remains close to 0%.
In September, the Fed announced that America should expect at least two Fed rate hikes in 2022. Economists predict these increases will be sooner than anticipated as the consumer price inflation continues to skyrocket.
Bottom Line: Borrowing is going to become more expensive. Together, a higher interest rate and increase in cost of raw materials can spell trouble for many businesses down the line. |
Our 7 Recommendations to Combat Inflation In Your Business
Here at U-Nique Accounting, we help business owners across retail & E-commerce, manufacturing, hospitality, and various other industries tackle the impacts of inflation head-on.
At a difficult time such as this one, we want to help as many businesses as we can.
Continue reading….



